Bootstrap Grid Table
Intro
Bootstrap features a great mobile-first flexbox grid solution for building designs of all forms and proportions . It's built on a 12 column arrangement and has multiple tiers, one for each and every media query range. You can work with it along with Sass mixins or of the predefined classes.
Probably the most necessary part of the Bootstrap system making it possible for us to create responsive page interactively enhancing in order to constantly provide the width of the display screen they become shown on still looking beautifully is the so called grid system. The things it basically works on is providing us the capability of generating complex layouts merging row and also a specific variety of column features maintained in it. Think that the obvious width of the display screen is separated in twelve matching parts vertically.
The best way to employ the Bootstrap grid:
Bootstrap Grid Tutorial employs a set of rows, columns, and containers to style and also adjust content. It's developed with flexbox and is entirely responsive. Listed here is an illustration and an in-depth look at ways the grid comes together.
The mentioned above scenario develops three equal-width columns on little, medium, big, and extra big devices employing our predefined grid classes. Those columns are centralized in the webpage along with the parent
.containerHere's how it works:
- Containers deliver a methods to focus your site's items. Use
.container.container-fluid- Rows are horizontal bunches of columns which provide your columns are really aligned correctly. We use the negative margin method upon
.row- Web content ought to be installed in columns, and only columns can be immediate children of rows.
- Thanks to flexbox, grid columns without having a established width will promptly design having identical widths. For example, four instances of
.col-sm- Column classes reveal the number of columns you want to use from the possible 12 per row. { So, on the occasion that you would like three equal-width columns, you are able to work with
.col-sm-4- Column
widths- Columns have horizontal
paddingmarginpadding.no-gutters.row- There are 5 grid tiers, one for every responsive breakpoint: all breakpoints (extra little), little, standard, large, and extra large size.
- Grid tiers are based on minimum widths, signifying they apply to that tier and all those above it (e.g.,
.col-sm-4- You are able to work with predefined grid classes as well as Sass mixins for additional semantic markup.
Recognize the restrictions and also failures about flexbox, such as the incapability to apply a number of HTML features such as flex containers.
Seems fantastic? Wonderful, let us proceed to viewing all that in an example. ( see post)
Bootstrap Grid Example possibilities
Typically the column classes are actually something like that
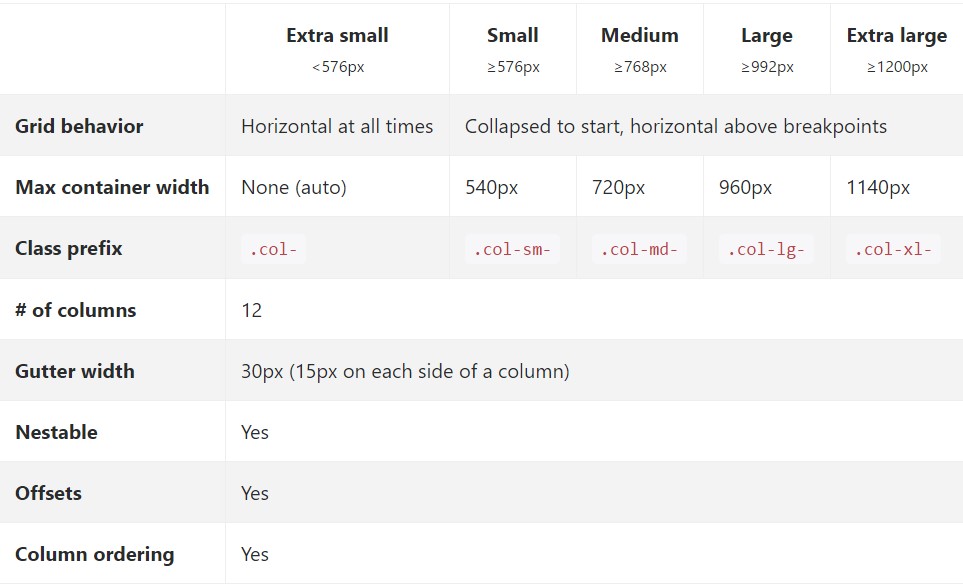
.col- ~ grid size-- two letters ~ - ~ width of the element in columns-- number from 1 to 12 ~.col-When it comes to the Bootstrap Grid Panel scales-- all the actually possible widths of the viewport ( or else the exposed area on the display screen) have been parted to five variations just as follows:
Extra small-- widths under 544px or 34em ( that happens to be the default measuring unit for Bootstrap 4
.col-xs-*Small – 544px (34em) and over until 768px( 48em )
.col-sm-*Medium – 768px (48em ) and over until 992px ( 62em )
.col-md-*Large – 992px ( 62em ) and over until 1200px ( 75em )
.col-lg-*Extra large-- 1200px (75em) and whatever bigger than it
.col-xl-*While Bootstrap uses
emrempxView the way in which aspects of the Bootstrap grid system work across various tools with a convenient table.
The brand new and several from Bootstrap 3 here is one added width range-- 34em-- 48em being simply designated to the
xsEach of the aspects styled utilizing a particular viewport width and columns preserve its overall size in width when it comes to this viewport and all above it. Whenever the width of the screen goes under the specified viewport size the features stack over each other packing the whole width of the view .
You can likewise appoint an offset to an element via a specified number of columns in a specific display screen sizing and over this is completeded with the classes
.offset- ~ size ~ - ~ columns ~.offset-lg-3.col- ~ size ~-offset- ~ columns ~A couple factors to take into account anytime designing the markup-- the grids consisting of rows and columns ought to be placed within a
.container.container.container-fluidDirect offspring of the containers are the
.rowAuto configuration columns
Implement breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Put in any quantity of unit-less classes for each breakpoint you require and every column will certainly be the equivalent width.
Equivalent width
For example, listed below are two grid designs that apply to each and every device and viewport, from
xs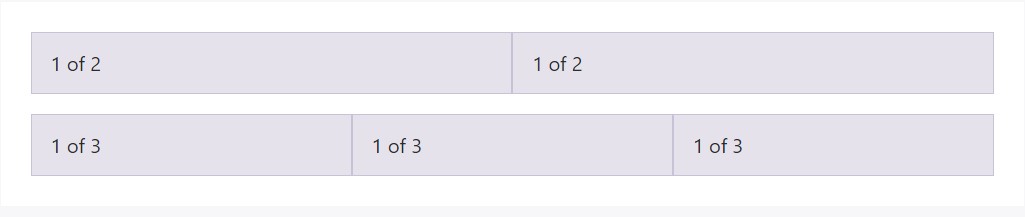
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Initiating one column width
Auto-layout for the flexbox grid columns as well signifies you can easily put the width of one column and the others will instantly resize around it. You may utilize predefined grid classes ( just as indicated below), grid mixins, as well as inline widths. Bear in mind that the some other columns will resize despite the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable width material
Applying the
col- breakpoint -auto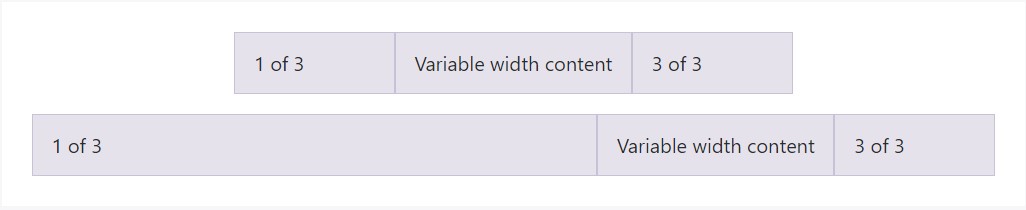
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Equal width multi-row
Create equal-width columns which go across multiple rows with filling in a
.w-100.w-100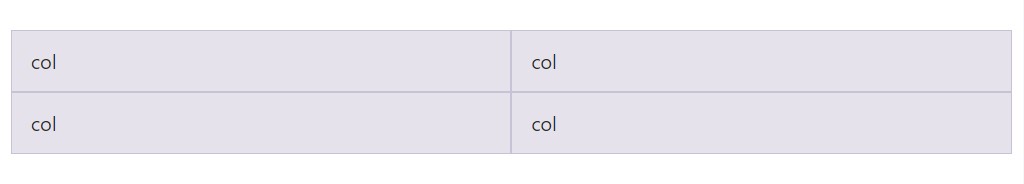
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>Responsive classes
Bootstrap's grid involves five tiers of predefined classes intended for building complex responsive designs. Individualize the size of your columns on extra small, small, medium, large, or else extra large gadgets however you please.
All breakpoints
Intended for grids that are the identical from the tiniest of gadgets to the largest, use the
.col.col-*.col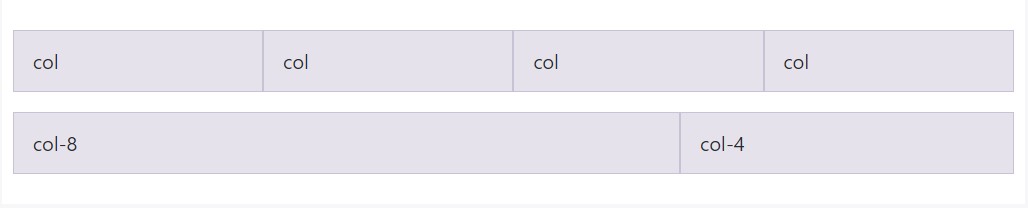
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8">col-8</div>
<div class="col-4">col-4</div>
</div>Loaded to horizontal
Employing a single package of
.col-sm-*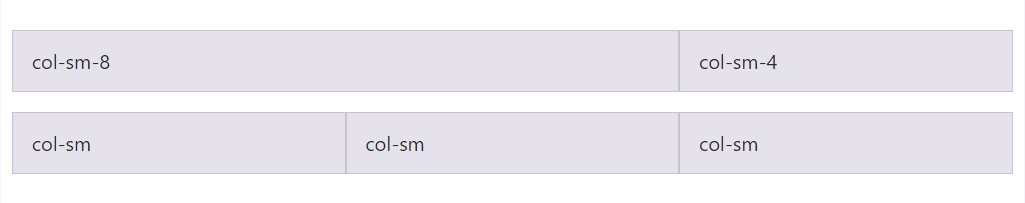
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-8">col-sm-8</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">col-sm-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
</div>Combine and suit
Really don't prefer your columns to just simply pile in several grid tiers? Work with a mixture of numerous classes for each and every tier as desired. Check out the sample below for a more suitable idea of exactly how all of it functions.
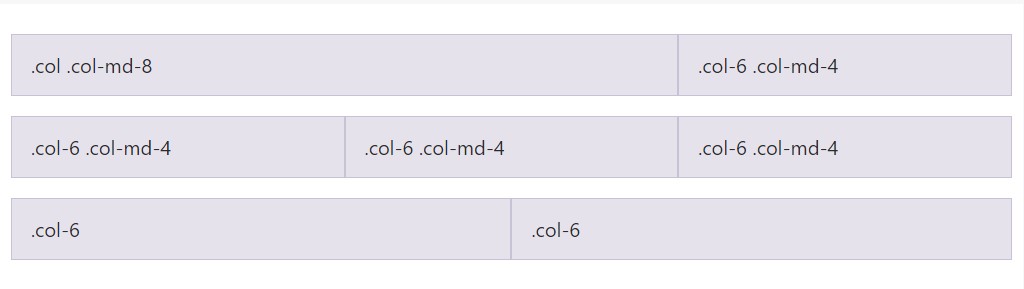
<div class="row">
<div class="col col-md-8">.col .col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<!-- Columns start at 50% wide on mobile and bump up to 33.3% wide on desktop -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<!-- Columns are always 50% wide, on mobile and desktop -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
</div>Placement
Use flexbox alignment utilities to vertically and horizontally fix columns. ( additional hints)
Vertical positioning
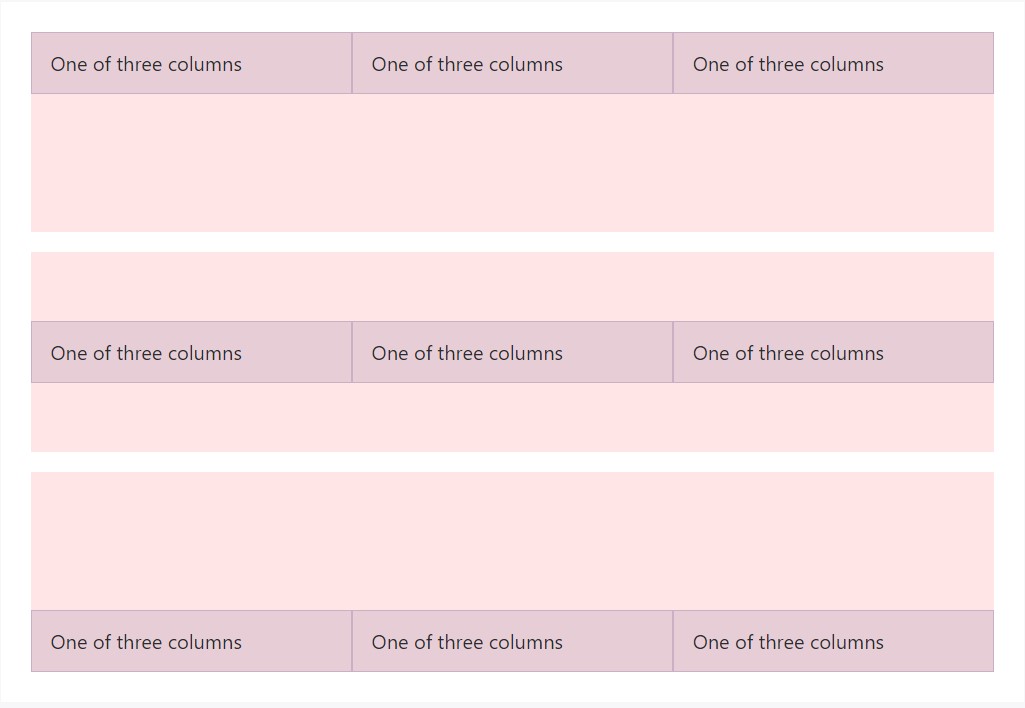
<div class="container">
<div class="row align-items-start">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row align-items-center">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row align-items-end">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
</div>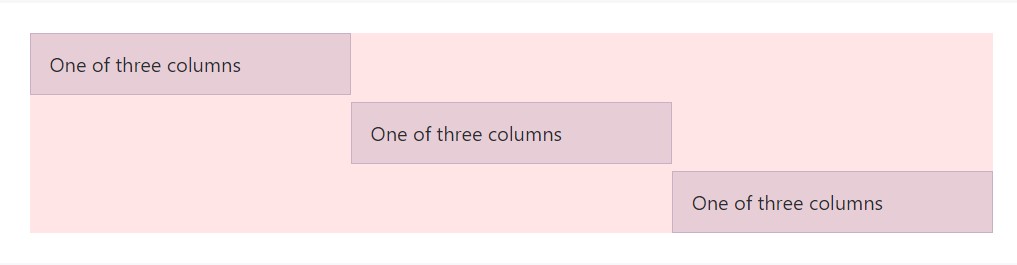
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col align-self-start">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col align-self-center">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col align-self-end">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
</div>Horizontal arrangement

<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-start">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-center">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-end">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-around">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-between">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
</div>No margins
The gutters among columns inside our predefined grid classes may be taken away with
.no-guttersmargin.rowpaddingHere is simply the source code for making these kinds of designs. Take note that column overrides are scoped to only the primary children columns and are intended via attribute selector. While this provides a more particular selector, column padding can still be additional customized together with spacing utilities.
.no-gutters
margin-right: 0;
margin-left: 0;
> .col,
> [class*="col-"]
padding-right: 0;
padding-left: 0;In practice, here's precisely how it looks like. Keep in mind you are able to remain to apply this along with all other predefined grid classes ( involving column sizes, responsive tiers, reorders, and much more ).

<div class="row no-gutters">
<div class="col-12 col-sm-6 col-md-8">.col-12 .col-sm-6 .col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>Column wrapping
Supposing that over 12 columns are positioned within a single row, each and every group of additional columns will, as being one unit, wrap onto a new line.

<div class="row">
<div class="col-9">.col-9</div>
<div class="col-4">.col-4<br>Since 9 + 4 = 13 > 12, this 4-column-wide div gets wrapped onto a new line as one contiguous unit.</div>
<div class="col-6">.col-6<br>Subsequent columns continue along the new line.</div>
</div>Reseting of the columns
Having the number of grid tiers available, you're expecteded to run into problems where, at particular breakpoints, your columns really don't clear pretty appropriate being one is taller than the other. To deal with that, utilize a combination of a
.clearfix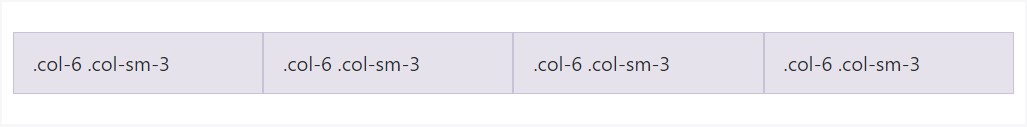
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<!-- Add the extra clearfix for only the required viewport -->
<div class="clearfix hidden-sm-up"></div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
</div>In addition to column clearing at responsive breakpoints, you may likely need to reset offsets, pushes, or pulls. View this practical in the grid illustration.

<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-5 col-md-6">.col-sm-5 .col-md-6</div>
<div class="col-sm-5 offset-sm-2 col-md-6 offset-md-0">.col-sm-5 .offset-sm-2 .col-md-6 .offset-md-0</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-5 col-lg-6">.col.col-sm-6.col-md-5.col-lg-6</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-5 offset-md-2 col-lg-6 offset-lg-0">.col-sm-6 .col-md-5 .offset-md-2 .col-lg-6 .offset-lg-0</div>
</div>Re-ordering
Flex order
Make use of flexbox utilities for regulating the visual order of your material.
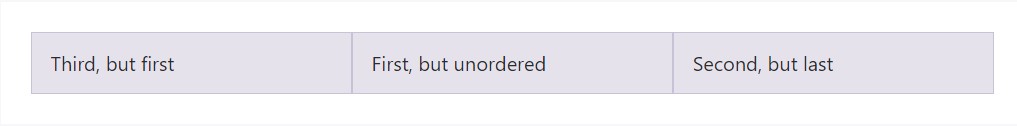
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col flex-unordered">
First, but unordered
</div>
<div class="col flex-last">
Second, but last
</div>
<div class="col flex-first">
Third, but first
</div>
</div>
</div>Countering columns
Shift columns to the right applying
.offset-md-**.offset-md-4.col-md-4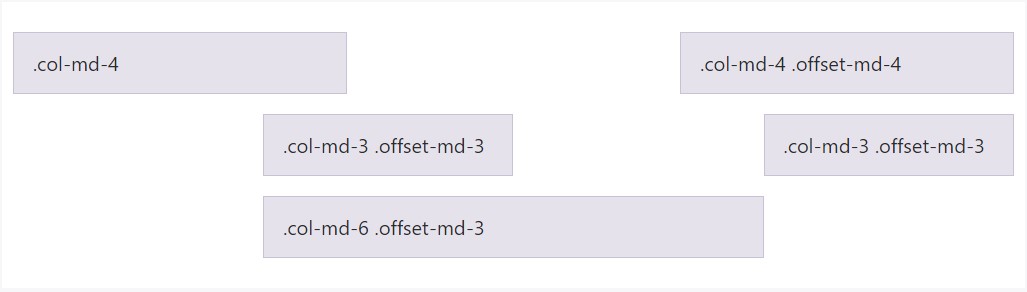
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 offset-md-4">.col-md-4 .offset-md-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 offset-md-3">.col-md-3 .offset-md-3</div>
<div class="col-md-3 offset-md-3">.col-md-3 .offset-md-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3">.col-md-6 .offset-md-3</div>
</div>Pulling and pushing
Conveniently change the order of our integrated grid columns with
.push-md-*.pull-md-*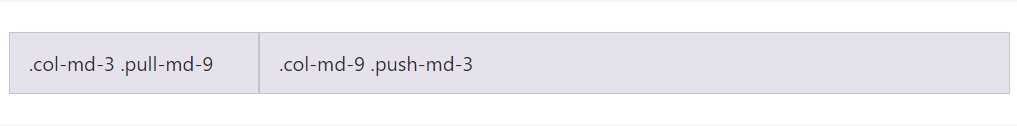
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-9 push-md-3">.col-md-9 .push-md-3</div>
<div class="col-md-3 pull-md-9">.col-md-3 .pull-md-9</div>
</div>Web content positioning
To roost your material with the default grid, provide a brand-new
.row.col-sm-*.col-sm-*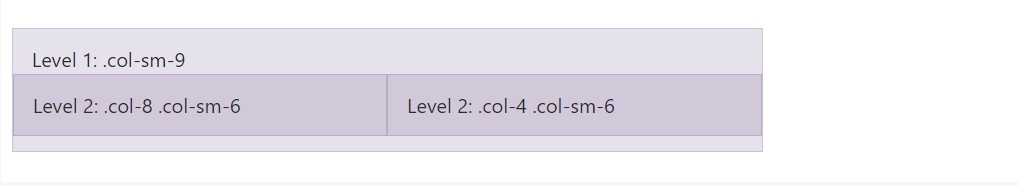
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Making the most of Bootstrap's origin Sass data
Whenever putting to use Bootstrap's origin Sass data, you have the option of applying Sass variables and mixins to make customized, semantic, and responsive page layouts. Our predefined grid classes apply these same variables and mixins to present a whole package of ready-to-use classes for quick responsive configurations .
Opportunities
Variables and maps determine the variety of columns, the gutter width, and also the media query point. We use these to produce the predefined grid classes detailed earlier, as well as for the custom-made mixins listed below.
$grid-columns: 12;
$grid-gutter-width-base: 30px;
$grid-gutter-widths: (
xs: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
sm: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
md: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
lg: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
xl: $grid-gutter-width-base // 30px
)
$grid-breakpoints: (
// Extra small screen / phone
xs: 0,
// Small screen / phone
sm: 576px,
// Medium screen / tablet
md: 768px,
// Large screen / desktop
lg: 992px,
// Extra large screen / wide desktop
xl: 1200px
);
$container-max-widths: (
sm: 540px,
md: 720px,
lg: 960px,
xl: 1140px
);Mixins
Mixins are employed along with the grid variables to bring in semantic CSS for individual grid columns.
@mixin make-row($gutters: $grid-gutter-widths)
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
@each $breakpoint in map-keys($gutters)
@include media-breakpoint-up($breakpoint)
$gutter: map-get($gutters, $breakpoint);
margin-right: ($gutter / -2);
margin-left: ($gutter / -2);
// Make the element grid-ready (applying everything but the width)
@mixin make-col-ready($gutters: $grid-gutter-widths)
position: relative;
// Prevent columns from becoming too narrow when at smaller grid tiers by
// always setting `width: 100%;`. This works because we use `flex` values
// later on to override this initial width.
width: 100%;
min-height: 1px; // Prevent collapsing
@each $breakpoint in map-keys($gutters)
@include media-breakpoint-up($breakpoint)
$gutter: map-get($gutters, $breakpoint);
padding-right: ($gutter / 2);
padding-left: ($gutter / 2);
@mixin make-col($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
flex: 0 0 percentage($size / $columns);
width: percentage($size / $columns);
// Add a `max-width` to ensure content within each column does not blow out
// the width of the column. Applies to IE10+ and Firefox. Chrome and Safari
// do not appear to require this.
max-width: percentage($size / $columns);
// Get fancy by offsetting, or changing the sort order
@mixin make-col-offset($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
margin-left: percentage($size / $columns);
@mixin make-col-push($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
left: if($size > 0, percentage($size / $columns), auto);
@mixin make-col-pull($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
right: if($size > 0, percentage($size / $columns), auto);Example use
You have the ability to reshape the variables to your own custom made values, or else simply just work with the mixins having their default values. Here is actually an example of applying the default configurations to produce a two-column layout with a divide between.
Check it out practical in this particular rendered illustration.
.container
max-width: 60em;
@include make-container();
.row
@include make-row();
.content-main
@include make-col-ready();
@media (max-width: 32em)
@include make-col(6);
@media (min-width: 32.1em)
@include make-col(8);
.content-secondary
@include make-col-ready();
@media (max-width: 32em)
@include make-col(6);
@media (min-width: 32.1em)
@include make-col(4);<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="content-main">...</div>
<div class="content-secondary">...</div>
</div>
</div>Customing the grid
Applying our built-in grid Sass maps and variables , it is definitely feasible to entirely customize the predefined grid classes. Switch the amount of tiers, the media query dimensions, and the container sizes-- and then recompile.
Gutters and columns
The variety of grid columns and also their horizontal padding (aka, gutters) may possibly be customized by using Sass variables.
$grid-columns$grid-gutter-widthspadding-leftpadding-right$grid-columns: 12 !default;
$grid-gutter-width-base: 30px !default;
$grid-gutter-widths: (
xs: $grid-gutter-width-base,
sm: $grid-gutter-width-base,
md: $grid-gutter-width-base,
lg: $grid-gutter-width-base,
xl: $grid-gutter-width-base
) !default;Opportunities of grids
Moving further the columns themselves, you can as well customise the amount of grid tiers. Supposing that you required simply three grid tiers, you 'd upgrade the
$ grid-breakpoints$ container-max-widths$grid-breakpoints: (
sm: 480px,
md: 768px,
lg: 1024px
);
$container-max-widths: (
sm: 420px,
md: 720px,
lg: 960px
);The instant producing any kind of changes to the Sass variables or maps , you'll need to save your adjustments and recompile. Doing this will out a brand new set of predefined grid classes for column widths, offsets, pushes, and pulls. Responsive visibility utilities definitely will likewise be up-dated to utilize the customized breakpoints.
Conclusions
These are truly the simple column grids in the framework. Working with particular classes we can certainly direct the specific components to span a defined number of columns depending on the definite width in pixels of the viewable zone in which the page gets revealed. And given that there are actually a plenty of classes defining the column width of the components rather than taking a look at every one it is certainly more useful to try to learn how they actually get constructed-- it is undoubtedly quite convenient to remember featuring simply just a few things in mind.
Check some on-line video short training regarding Bootstrap grid
Related topics:
Bootstrap grid official information
W3schools:Bootstrap grid tutorial
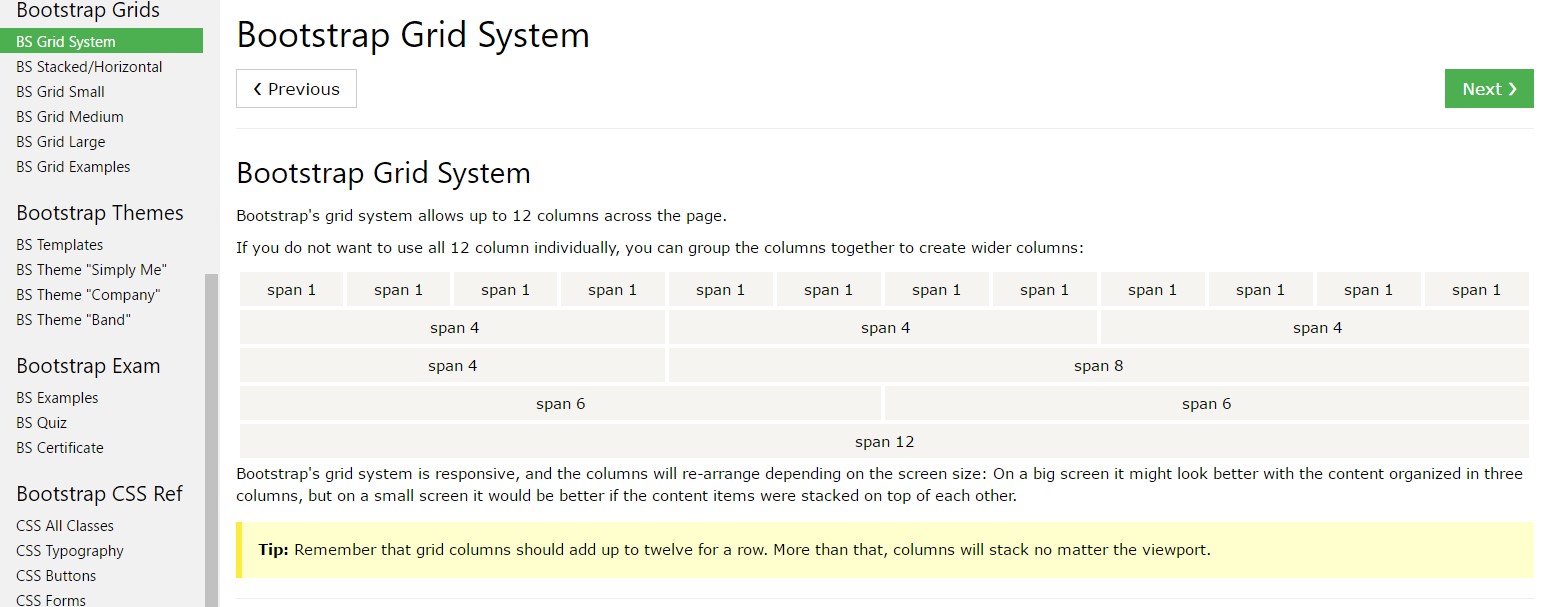
Bootstrap Grid column